- Centos Restart Sshd
- Restart Sshd Windows
- Mac Restart Sshd
- Restart Sshd Daemon
- Restart Sshd Service Ubuntu
Learn more about VMware vSphere 7, the world’s leading server virtualization software for containerized & existing enterprise applications. Sudo stop ssh sudo start ssh As it leverages upstart, this is The Best Way™ to do it, rather than using /etc/init.d/ssh, service, or invoking sshd directly. Make sure to run both commands; if you get an error on stop ssh, start ssh anyway and see what it says—the service could already be stopped.
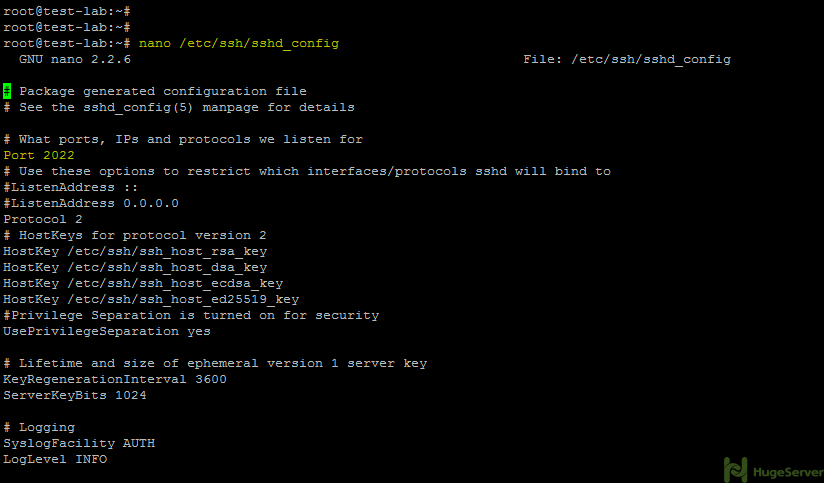
To restart SSH in solaris you can use the svcs command to view the current status of the service root@solaris:# svcs grep ssh online. Computer How To How To, Tutorial, Example, Review.
Centos Restart Sshd
Managing services is a key responsibility for sysadmins. There is no doubt that the transition between the older SysV method (using the service and chkconfig commands) and the newer systemd-based commands (such as systemctl) was controversial. In fact, many sysadmins still have very strong feelings one way or the other.
The reality is that many distributions, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) included, have begun managing services with systemd. Hence, you and I need to know how to work with the systemctl management command.
More Linux resources
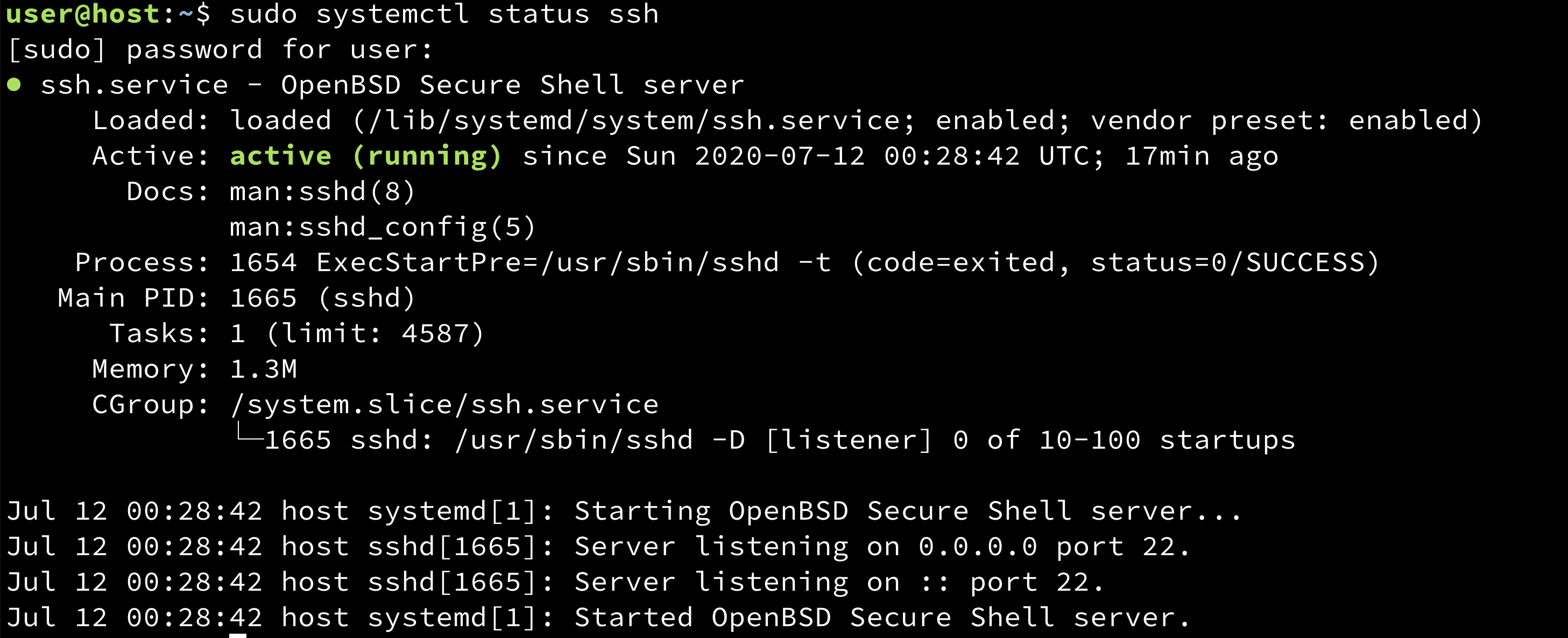
I'm not the kind of author/trainer/admin that assumes everyone is advanced. With that in mind, I'm going to aim this article at the folks who need a fundamental and straightforward explanation of how and when to use the more common systemctl subcommands. At the end, I also provide a great trick for quickly displaying all the systemctl subcommands.

Note: The systemctl man page refers to the second word in the string as a 'command,' which seems somewhat confusing. I will refer to systemctl itself as a command, then the string following it as a subcommand. The argument is the name of the service and occupies the third position in the syntax.

Here is a syntax example:
Restart Sshd Windows
I'll demonstrate how and when to use systemctl. Most of my examples use the common sshd service.
Mac Restart Sshd
[ Readers also enjoyed: How I learned to stop worrying and love systemd ]
Open and unlock 1Password, select the Login item for the website, then select Edit. Select to the right of the field (Shift + Enter) and choose One-Time Password. Click and choose “From my screen” to scan the QR code. If you can’t scan the QR code, make sure it’s visible when you minimize 1Password. Microsoft Authenticator Although 1Password can be used to store one-time passwords for other services where you use two-factor authentication, it’s important to use a different authenticator app to store the authentication codes for your 1Password account. Storing them in 1Password would be like putting the key to a safe inside the safe itself. Add multiple accounts. Protect all of your accounts with two-step verification. The app also helps you secure all of your online accounts by using the industry standard time-based OTP (one-time password. Use time-based, one-time passcodes The Microsoft Authenticator app also supports the industry standard for time-based, one-time passcodes (also known as TOTP or OTP). Because of that, you can add any online account that also supports this standard to the Microsoft Authenticator app. This will help keep your other online accounts secure. One password authenticator.
Restart Sshd Daemon
Service status
Restart Sshd Service Ubuntu
The best place to start is to understand the current functionality of the service. I'll begin with the most simple approach, the use of the status subcommand:
